Table of Content
Employees who work at home may no longer use the home business tax deduction. The owner must use the space regularly and exclusively for business purposes and it must usually be their principal place of business. Expenses that relate to a separate structure not attached to the home will qualify for a home office deduction. It will qualify only if the structure is used exclusively and regularly for business.
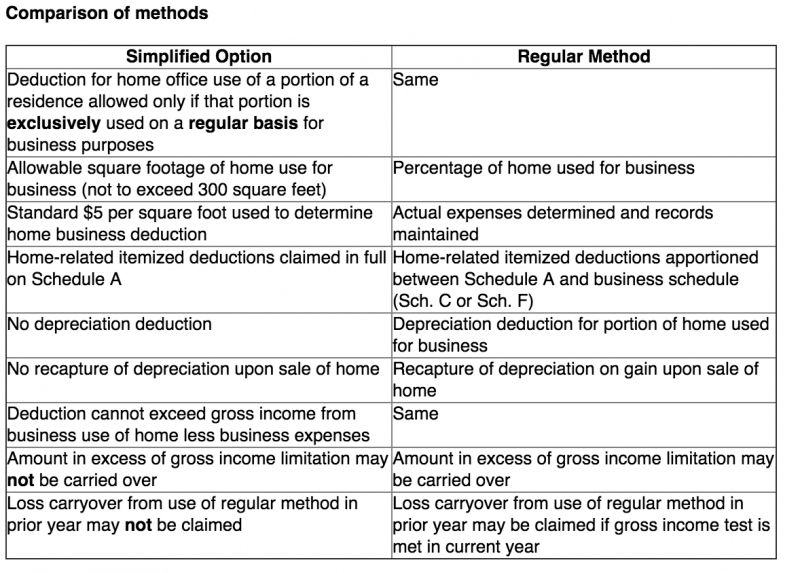
The regular method allows for carrying over the deduction for eligible filers. Our Full Service Guarantee means your tax expert will find every dollar you deserve. Your expert will only sign and file your return if they know it's 100% correct and you are getting your best outcome possible. If you get a larger refund or smaller tax due from another tax preparer, we'll refund the applicable TurboTax Live Full Service federal and/or state purchase price paid. To claim the home-office deduction in 2021, taxpayers must exclusively and regularly use part of their home or a separate structure on their property as their primary place of business.
Calculate your allowable deduction
This article will assist you with using the simplified method for Form 8829 home office deduction in Intuit ProConnect. Sign Up NowGet this delivered to your inbox, and more info about our products and services. If your business is in a federally declared disaster area during the year, you may be able to deduct casualty losses for your home business.
Good Company Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
Part 2: Figure your allowable deduction
Be sure to only use expenses for the months you were self-employed, or otherwise eligible, to calculate the deduction. Many people don’t realize they are eligible for home office tax deductions. If you’re self-employed, find out if you’re eligible for this tax break.
You need to figure out the percentage of your home devoted to your business activities, utilities, repairs, and depreciation. The simplified option has a rate of $5 a square foot for business use of the home. If an eligible taxpayer decides to use the simplified deduction method, they can use the number of months they worked from home to prorate the amount they can deduct. They can also choose to deduct a portion of actual expenses for the months they were eligible for the deduction. Over the past couple of years, COVID-19 has brought a work-from-home lifestyle to employees around the globe.
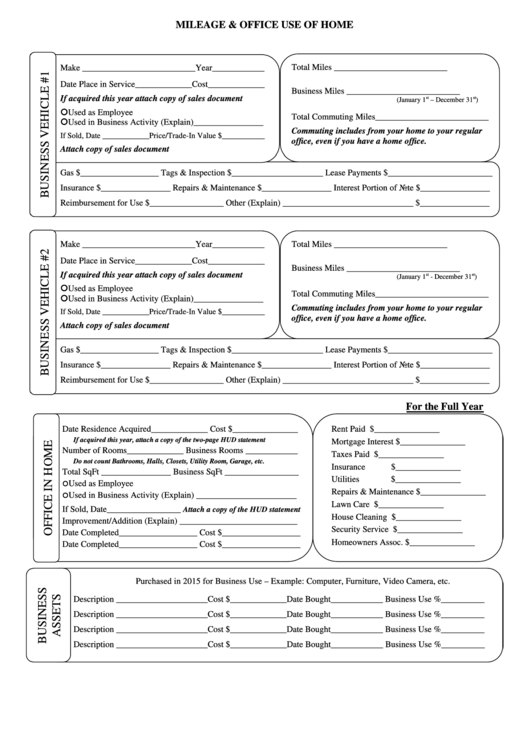
Depreciation of your home
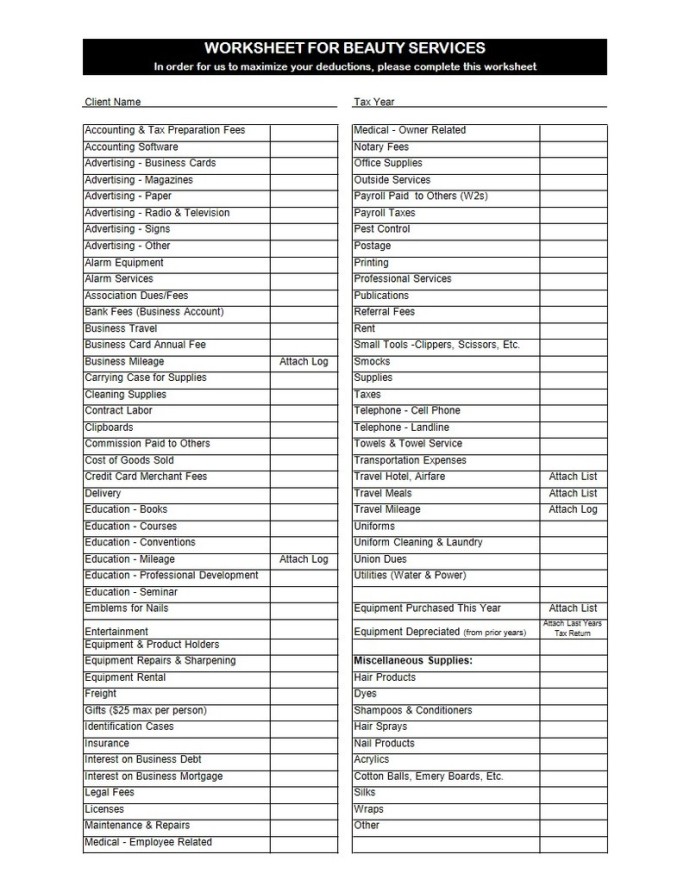
For example, if you use your car for business or rent equipment to use in your business, those costs could be deductible. If you run a home-based daycare business, there are a few extra lines to complete. You may need to use a special method to calculate your deduction, too. Check out the IRS Instructions for Form 8829 if you want more information on completing this form for a daycare. Since you use 10% of your home (2,000 total square feet / 200 home office square feet), your home office deduction using the regular method would be $800 ($8,000 x .10). The home office tax deduction is easy to claim but can be hard to defend.
Now, at tax time, it’s important for workers to understand the home office tax deduction requirements and the specific deductions they may be eligible to take on their tax forms. It’s easy to forget what direct and indirect expenses you’ll want to claim when taxes roll around. Home repairs that happened in January feel like a very distant memory over a year later. Keep a list and receipts of everything, both direct and indirect expenses, that you can use when filling out the form.
Home Office Tax Deductions: What You Need to Know
This will make things speedier once it comes time to sit down and fill out the form. IRS Form 8829 is one of two ways to claim a home office deduction on your business taxes. If your business qualifies for the home office deduction, you’ll file Form 8829 with your Schedule C, profit or loss from business. Deductible mortgage interest provided is limited to the percentage of your home dedicated solely to your business. For example, if only 15% of a square foot of a house is dedicated to business, then only 15% of household expenses can be used as a business deduction. With the regular method of calculating the home office deduction, your deduction can’t exceed your gross income derived from your business — same as with the simplified option.
The instructions for Form 8829 document from the IRS provides even more detailed guidance for each line item. In addition, taking the deduction could make it more difficult to sell your home in the future, if you own. That's because you can depreciate the value of your home office, which could create a tax event later when you sell. While employees who now work remotely may feel like they're missing out, the home-office deduction isn't generally leading to outsized savings for those who take it. There may be some confusion, as the home-office deduction was previously allowed for employees. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017, however, banned such workers from taking the deduction from 2018 to 2025.
Another thing to note is that certain expenses can only be used to the extent of your business income. If you have a loss from your home-based business, you can only deduct certain home office expenses. Just because you work from home does not mean you are eligible to take business or home office deductions. Regular W-2 employees are no longer able to deduct home office costs, and employers are not required to cover the costs of working remotely .
Beginning in 2013, the IRS introduced a new way of calculating the home office deduction called the simplified method. Under the simplified method, there’s no extensive calculation to make or additional receipts to keep. You simply take a standard deduction of $5 for every square foot of office space, up to 300 square feet. As so much of this form depends on using the business percentage of your home, get accurate measurements of your space done early. Measure the part of your home that qualifies for the deduction and look up the total square footage of your home on your county records.
Then you’ll separate out the value of the land and the value of the home . That’s because you only take depreciation on the building, not the land. Direct expenses are only related to the office portion of your home. If you need to repaint just your office, that’s a direct expense.

“Exclusive use” means you must use the specific space only for business purposes. The space can be part of a room and it doesn’t have to be physically marked off to qualify. You don’t have to meet the exclusive-use rule if you use that part of your home for storing inventory or product samples, or for a daycare facility. A taxpayer can also meet this requirement if administrative or management activities are conducted at the home and there is no other location to perform these duties. Therefore, someone who conducts business outside of their home but also uses their home to conduct business may still qualify for a home office deduction. Should you qualify for a deduction in respect of a home office; enter the amount calculated next to the source code in the “Other Deduction” container on your Income Tax Return.
You’ll then enter the depreciation percentage from the instructions on line 41. Multiply that percentage by the basis and you’ll get your allowable depreciation deduction. This part of Form 8829 can get really tricky — it’s now time to calculate the percentage of depreciation on your home you can include in your deduction calculation. This may influence which products we review and write about , but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services.


No comments:
Post a Comment